Identifying the sources and cycling of phosphorus (P) is particularly importantfor formulating effective P management strategies in inland water. The oxygen isotopic compositions of phosphate (δ18OP)are recognized as a promising tool to solve this problem. However, the application of δ18OPin freshwater sediment is currentlyconstrained by multipledifficulties.
Recently, Prof. Chen Jingan’s research teamfrom the theInstituteof Geochemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGCAS), presenteda novel pretreatment method for δ18OP analysisofsediment inorganic P pools. Specifically, the traditional Mg-inducedco-precipitation (MAGIC) method was replaced by introducing Zr-Oxidesgels with high selective adsorption function for phosphate.
Results showed that the new method has advantages of simple operation, lesstime-consuming, and high P recovery rates. Furthermore, the study emphasized the necessity of vacuum roasting following lyophilized Ag3PO4 to eliminate residual oxygen-containing impurities. Importantly,combining directsynthesis Ag3PO4 between KH2PO4 and AgNO3 with the Ag3PO4 obtained by the method revealed no stark oxygen isotopic fractionation of phosphate duringthe pretreatment processes.
This study was published in WaterResearch on July 22, 2024 with the title of “A novel pretreatment method foranalys is the oxygen isotopic compositions of inorganic phosphoruspools in freshwater sediment”.
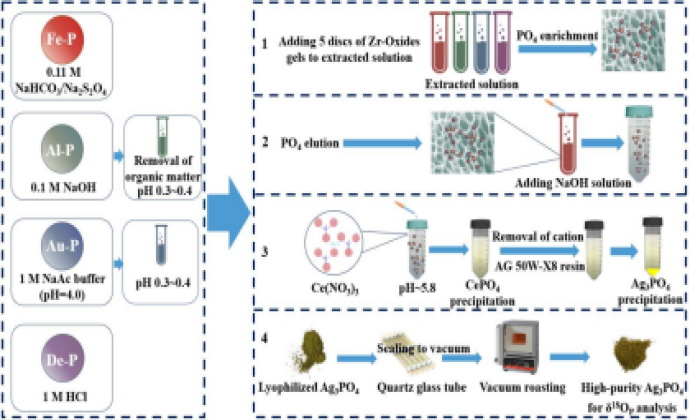
Fig.Purification steps for Ag3PO4 of different Pi poolsin sediment.
Contact:
Jin Zu xue
Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: jinzuxue@mail.gyig.ac.cn
(By Prof.Chen Jingan’s Group)