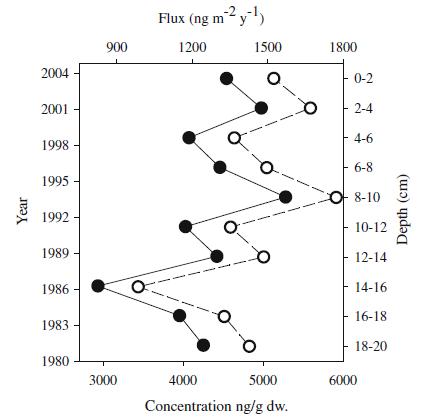
Fig. Vertical profile of PAHs assessed against depositional year and depth. Solid circles = concentrations; open circles = fluxes
Using data from a 25-year retrospective of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediment core from Lake Hongfeng, Southwest China, their possible sources and potential toxicologic significance were investigated. The total PAH concentrations (16 priority PAHs as proposed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency) in sediments ranged from 2936.1 to 5282.3 ng/g and gradually increased from the analyzed deeper sediments to surface sediments. PAHs were dominated by low molecular-weight components, especially phenanthrene (PHEN) and fluorene (FLU). However, a significantly increased number of high molecular-weight (HMW) PAHs was found in upper segments. The temporal trends of individual PAH species suggest that there may have been a change in energy use from low-to high-temperature combustion, especially after approximately 2001. PAH input to Lake Hongfeng originated mainly from domestic coal combustion and biomass burning, whereas fuel combustion characteristics have also been found in recent years. Sediment-quality assessment implied that potential adverse biologic impact could be a probability for most low-ring PAHs (including naphthalene, acenaphthylene, acenaphthylene, FLU, PHEN, and anthracene). Nevertheless, more concern should be paid to HMW PAHs in the future due to their rapidly increasing trends in upper sediments. Because only one core was analyzed in this study, more work is needed to confirm the sources and toxicity of PAHs in Lake Hongfeng.
| Publication name |
ACTA GEOLOGICA SINICA-ENGLISH EDITION Volume: 85 Issue: 3 Pages: 712-722 Published: JUN 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Guo, Jian-Yang; Wu, Feng-Chang; Zhang, Liang; Liao, Hai-Qing; Zhang, Run-Yu; Li, Wei; Zhao, Xiao-Li; Chen, She-Jun; Mai, Bi-Xian |
| Corresponding author |
WU Fengchang
wufengchang@vip.skleg.cn
1. Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China
2. Chinese Res Inst Environm Sci, Res Ctr Lake Ecoenvironm, State Environm Protect Key Lab Lake Pollut Contro, Beijing 100012, Peoples R China |