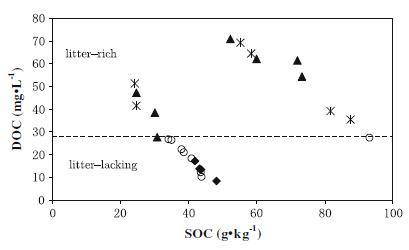
Fig. SOC and DOC content in surface soil. Filled triangle yellow soil with litter-lacking; filled diamond yellow soil with litter-lacking; open circle limestone soil with litter-lacking; asterisk limestone soil with litter-rich
There is considerable discussion and uncertainty in the literature regarding the importance of fresh litter versus older soil organic matter as sources of soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in forest floor. In this study, the differences of organic carbon concentration and stable isotope composition were analyzed under different background conditions to identify the origins of DOC in forest soil. The data show that there is no significant difference in SOC content between these collected soil samples (P > 0.05), but the litter-rich surface soils have relatively higher DOC concentration than the litter-lacking (P < 0.01) ones, and the delta C-13 values of DOC (delta C-13(DOC)) are closer to delta C-13 of litter than delta C-13 values of SOC (delta C-13(SOC)). In the litter-lacking surface soil samples, the range of delta C-13(DOC) is between delta C-13(SOC) and delta C-13 of dominant plant leaves. These results suggest that DOC mainly derive from litter in the litter-rich surface soil with, and the main path of DOC sources may change with surrounding conditions. In addition, delta C-13(SOC) and delta C-13(DOC) become more positive, and the absolute values of Delta (delta C-13(DOC) - delta C-13(SOC)) decrease with depth in the soil profiles, which indicate that the percentage of DOC below 5 cm, derived from degradation of humus, may increase with soil depth.
| Publication name |
ENVIRONMENTAL EARTH SCIENCES Volume: 63 Issue: 4 Pages: 723-730 Published: JUN 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Tu, Cheng-Long; Liu, Cong-Qiang; Lu, Xiao-Hui; Yuan, Ju; Lang, Yun-Cha |
| Corresponding author |
LIU Congqiang
liucongqiang@vip.skleg.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Inst Geochem, 46 Guanshui Rd, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Peoples R China |
View here for the Full Text from the publisher