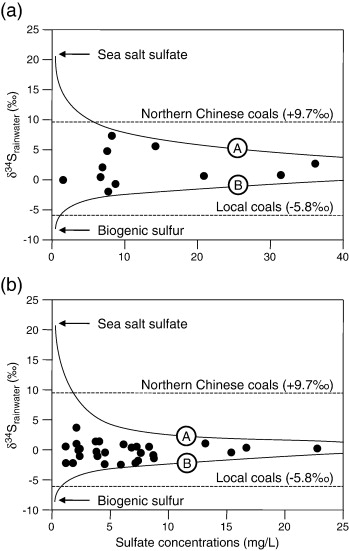
Figure The δ34S values vs. sulfate concentrations in rainwater at NNU (a) and QH (b) compared to a ternary mixing model. Curve A: mixing between anthropogenic sulfur with a δ34S value of about + 3‰ (a) or + 1‰ (b) and seawater sulfate with a δ34S value of + 21‰; Curve B: mixing between pollutant sulfate with a δ34S value of about 0‰ (a) or − 0.5‰ (b) and biogenic sulfur with a δ34S value of − 8‰.
Sulfur source identification previously reported has been based on sulfur isotopic ratios in either rainwater or mosses. The delta S-34 values of rainwater sulfate and the epilithic moss Haplocladium microphyllum in Nanchang region (China) were determined for comparisons and used to delineate atmospheric sulfur sources. At the urban and rural sites, similar mean delta S-34 values were observed between rainwater sulfate (+1.6 parts per thousand and -0.2 parts per thousand, respectively) and epilithic mosses (+1.7 parts per thousand and +0.6 parts per thousand, respectively), suggesting that mosses acquire delta S-34 values similar to those found for rainwater sulfate. This has further demonstrated that moss delta S-34 signatures hold valuable source-specific information as rainwater delta S-34 values do. The delta S-34 values of both rainwater sulfate and epilithic mosses indicated that atmospheric sulfur in Nanchang region was mainly associated with coal combustion. The lower delta S-34 values at the rural site can be explained by higher contribution of local coals (lower delta S-34 values relative to those of north Chinese coals) and biogenic sulfur. (C) 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
| Publication name |
SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT Volume: 409 Issue: 11 Pages: 2127-2132 Published: MAY 1 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Xiao, Hua-Yun; Zhu, Ren-Guo; Lin, Bi-Na; Liu, Cong-Qiang |
| Corresponding author |
XIAO Huayun
xiaohuayun@vip.skleg.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |