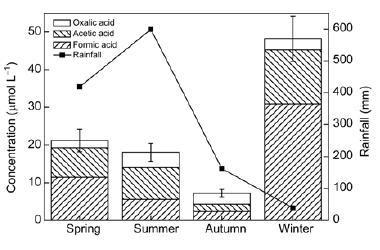
Figure Seasonal variations of rainfall (mm) and volume-weighted average (VWA) concentrations (μmol/L) of organic acids in precipitation collected at the sampling site.
Low molecular weight (LMW) organic acids are important and ubiquitous chemical constituents in the atmosphere. A comprehensive study of the chemical composition of precipitation was carried out from June 2007 to June 2008 at a rural site in Anshun, in the west of Guizhou Province, China. During this period, 118 rainwater samples were collected and the main LMW carboxylic acids were determined using ion chromatography. The average pH of rainwater was 4.89 which is a typical acidic value. The most abundant carboxylic acids were formic acid (volume weight mean concentration: 8.77 mu mol L-1) and acetic acid (6.90 mu mol L-1), followed by oxalic acid (2.05 mu mol L-1). The seasonal variation of concentrations and wet deposition fluxes of organic acids indicated that direct vegetation emissions were the main sources of the organic acids. Highest concentrations were observed in winter and were ascribed to the low winter rainfall and the contribution of other air pollution sources northeast of the study area. The ratio of formic and acetic acids in the precipitation ([F/A] (T) ) was proposed as an indicator of pollution source. This suggested that the pollution resulted from direct emissions from natural or anthropogenic sources. Comparison with acid precipitation in other urban and rural areas in Guizhou showed that there was a decreasing contribution of LMW organic acids to free acidity and all anions in rainwater from urban to remote rural areas. Consequently, it is necessary to control emissions of organic acids to reduce the frequency of acid rain, especially in rural and remote areas.
| Publication name |
CHINESE SCIENCE BULLETIN Volume: 56 Issue: 10 Pages: 1005-1010 Published: APR 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Zhang YanLin; Lee XinQing; Cao Fang; Huang DaiKuan |
| Corresponding author |
ZHANG Yanlin
dryanlinzhang@gmail.com,xinqinglee@hotmail.com
1. Chinese Acad Sci, Guangzhou Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Organ Geochem, Guangzhou 510640, Guangdong Peoples R China
2. Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |