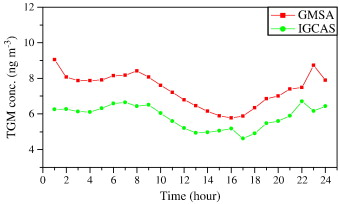
Fig. Diurnal variations of TGM concentrations in different sites of Guiyang, China.
Atmospheric mercury (Hg) species were measured in Guiyang City, the capital of Guizhou province, southwestern China at the Guiyang Monitoring Station Agency (GMSA) from September to November 2008 and at the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGCAS) during February, May, and July, 2009. Monitoring results found elevated concentrations of all three Hg species in ambient air in Guiyang. Large temporal and spatial variation patterns in the resulting data were also obtained. The overall average TGM concentrations at the GMSA and IGCAS sampling sites were 7.4 +/- 4.8 ng m(-3) and 6.2 +/- 5.1 ng m(-3), respectively. The average Hg(p) and RGM concentrations at GMSA were 1330 pg m(-3) and 24 pg m(-3), and at IGCAS were 250 pg m(-3) and 19 pg m(-3), respectively. It is hypothesized that local anthropogenic sources and the seasonal variability result in the high degree of spatial and temporal variability. (C) 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved..
| Publication name |
ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY Volume: 74 Issue: 3 Pages: 473-479 Published: MAR 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Liu, Na; Qiu, Guangle; Landis, Matthew S.; Feng, Xinbin; Fu, Xuewu; Shang, Lihai |
| Corresponding author |
QIU Guangle
qiuguangle@vip.skleg.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |