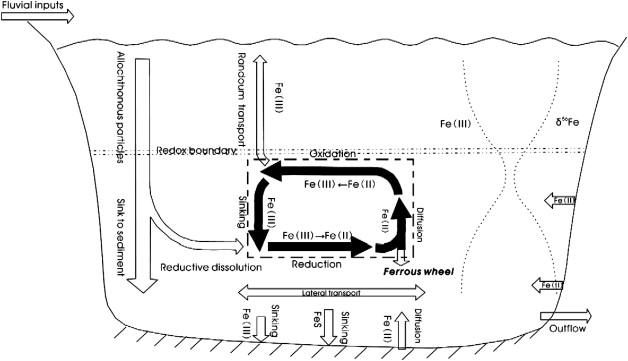
Fig. The “ferrous wheel” near redox boundary (modified from [Davison, 1985] and [Davison, 1993]).
Iron isotope compositions of suspended particulate matters (SPM) collected from the Aha Lake, an artificial lake in the karst area of Yun-Gui Plateau, and its tributaries in summer and winter were investigated for our understanding of the behavior of Fe isotopes during iron biogeochemical cycling in lake. delta Fe-56 values of SPM display statistically negative shift relative to IRMM-014. Samples from the lake display a range from -1.36%. to -0.10% in summer and from -0.30%, to -0.07 parts per thousand in winter, while river samples vary from -0.88 parts per thousand to -0.07 parts per thousand, in summer and from -0.35 parts per thousand. to -0.03 parts per thousand in winter. The average iron isotope composition of aerosol samples is +0.10 parts per thousand, which is very similar to that of igneous rocks (0.09 parts per thousand). The SPM in most rivers and water column showed seasonal variation in delta Fe-56 value: the delta Fe-56 values of SPM in summer were lower than in winter. The seasonal variation in delta Fe-56 value of the riverine SPM should be ascribed to the change in source of particulate Fe and geochemical process in the watershed: More particulate Fe was leached from soil and produced by weathering of pyrite widely distributed in coal-containing strata. It is suggested that both allochthonous inputs and the redox iron cycling control the variations of delta Fe-56 values for SPM in lake.
During summer stratification, an Fe cycle named "ferrous wheel" is established near the redox boundary where the upwardly diffusing Fe(II) is oxidized and the reactive Fe oxides formed will continuously sink back into the reduction zone to complete the cycle. The delta Fe-56 values for SPM reach the minima, -0.88 parts per thousand, for DB station and -1.36 parts per thousand. for LJK station, just near the redox boundary as a result of the Fe cycling, where a rough 45% to 76% of Fe in these particles was produced by the repetitive cycle. Due to random transportation and diffusion, delta Fe-56 values of the particles near the redox zone distributed into approximately a Gaussian shape. The good negative correlation existed between delta Fe-56 values and Fe/Al ratios for DB station, suggesting that they together can be used as good indicators of the redox-driven Fe transformations. (C) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
| Publication name |
CHEMICAL GEOLOGY Volume: 280 Issue: 1-2 Pages: 170-179 Published: JAN 7 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Song, Liuting; Liu, Cong-Qiang; Wang, Zhong-Liang; Zhu, Xiangkun; Teng, Yanguo; Liang, Lili; Tang, Suohan; Li, Jin |
| Corresponding author |
LIU Congqiang
liucongqiang@vip.skleg.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |