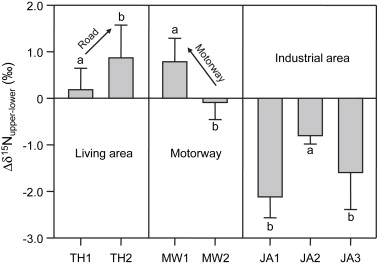
Fig. The ∆δ15N values (∆δ15N = δ15Nupper − δ15Nlower) of camphor leaves between upper and lower canopies in Nanchang City. Different uppercase letters denote means found to be statistically different by the Tukey-HSD test with LSD between sampling sites.
Nitrogen isotopic composition of new, middle-aged and old camphor leaves in upper and lower canopies has been determined in a living area, near a motorway and near an industrial area (Jiangan Chemical Fertilizer Plant). We found that at sites near roads, more positive delta N-15 values were observed in the camphor leaves, especially in old leaves of upper canopies, and Delta delta N-15 = delta N-15(upper) - delta N-15(lower) > 0, while those near the industrial area had more negative delta N-15 values and Delta delta N-15 < 0. These could be explained by two isotopically different atmospheric N sources: greater uptake from isotopically heavy pools of atmospheric NOx by old leaves in upper canopies at sites adjacent to roads, and greater uptake of N-15-depleted NHy in atmospheric deposition by leaves at sites near the industrial area. This study presents novel evidence that N-15 natural abundance of camphor leaves can be used as a robust indicator of atmospheric N sources. (C) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
| Publication name |
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION Volume: 159 Issue: 2 Pages: 363-367 Published: FEB 2 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Xiao, Hua-Yun, Wu, Liang-Hong, Zhu, Ren-Guo, Wang, Yan-Li, Liu, Cong-Qiang |
| Corresponding author |
XIAO Hua-Yun
xiaohuayun@vip.skleg.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Inst Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |
View here for the full text from the publisher
 |
 |
|