| Mercury and other metal and metalloid soil contamination near a Pb/Zn smelter in east Hunan province, China |
TEXT SIZE: A A A |
| |
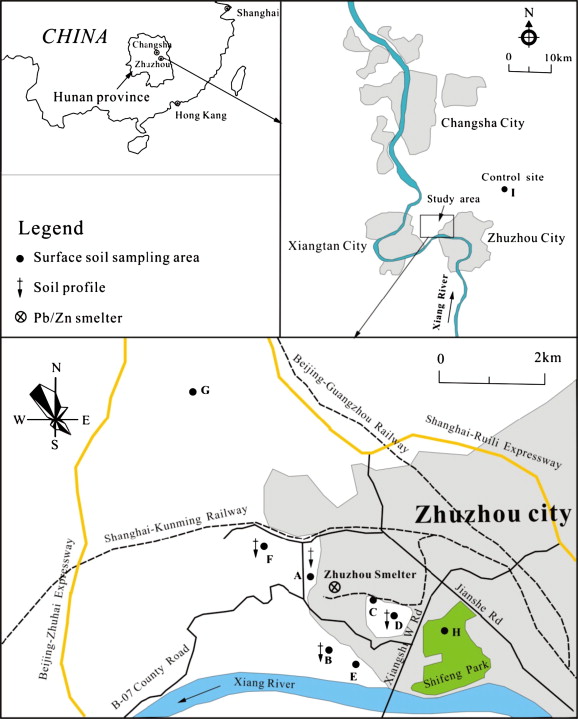
Fig. Location of the sampling sites.
The spatial distributions of contaminant metals (Hg, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu) and a metalloid (As) in vegetable plots and paddy fields located near a large scale Pb/Zn smelter in Hunan province, China, were investigated. Soil located 4 km from the smelter was severely contaminated, with maximum concentrations of Hg, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu and As as high as 2.89, 1200, 3350, 41.1, 157 and 93 mg kg(-1), respectively. Concentrations of soil metal and As decreased with distance in the dominant wind direction. Single-factor assessment indicated pollution levels of Hg, Pb, Zn and Cd were most severe, while pollution levels for Cu and As were less severe. Results from a potential ecological risk assessment indicated high risk associated with the soil within a 4 km radius, with the contribution for each contaminant calculated as follows: Cd (70.0%), Hg (19.4%), Pb (4.8%), As (3.0%), Cu (1.7%) and Zn (1.1%). The forest soil in the nearby city park was also affected by the atmospheric depositions from smelting activities. Soil profiles demonstrated the pollutants were mostly accumulated in the upper 20 cm layer. Contamination of the topsoil with Hg, Pb, Zn, Cd, Cu and As indicated remediation should be considered. (C) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
| Publication name |
APPLIED GEOCHEMISTRY Volume: 26 Issue: 2 Pages: 167-173 Published: FEB 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Li, Zhonggen; Feng, Xinbin; Li, Guanghui; Bi, Xiangyang; Sun, Guangyi; Zhu, Jianming; Qin, Haibo; Wang, Jianxu |
| Corresponding author |
FENG, Xinbin
fengxinbin@vip.skleg.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |
View here for the full text from the publisher
 |
 |
|
|