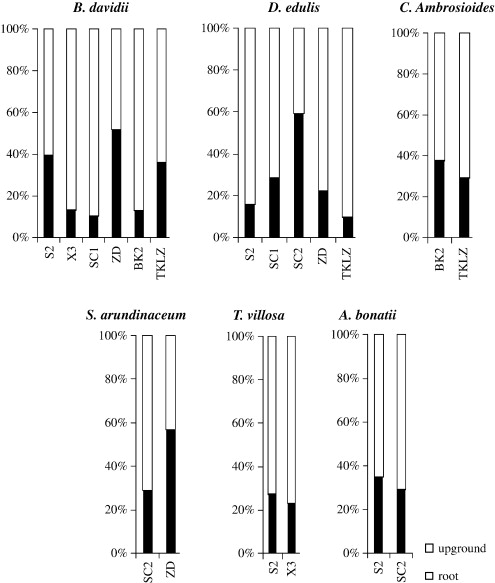
Fig. 6. Percent concentration cumulus histogram of Sb in upground part and root in six plants.
Antimony (Sb) distribution and accumulation in plants in Xikuangshan Sb deposit area, the only one super-large Sb deposit in the world, Hunan. China were investigated. Results show that soils were severely polluted with the average Sb concentrations up to 5949.20 mg kg(-1) Sb widely occurred in 34 plants with various concentrations ranging from 3.92 mg kg(-1) to 143.69 mg kg(-1) Equisetaceae family has the highest concentration (98.23 mg kg(-1)) while Dryopteridacea family has the lowest one (6.43 mg kg(-1)). H. ramosissima species of Equisetaceae family had the highest Sb average concentration of 98.23 mg kg(-1) and P. vittata species of Pteridaceae family showed advantage of accumulating Sb from the contaminated environment (Biological Accumulation Coefficient, BAC=0.08). Almost all species enriched Sb in their upground part such as shoot, leaf and flower (Biological Transfer Coefficient, BTC>1), which may attribute to the high acropetal coefficient and Sb transformation from the atmosphere to the plants. P. phaseoloides and D. indicum showed predominantly accumulation of Sb in the upground part with BTC of 6.65 and 5.47, respectively.
From the low bioavailable fraction in soils and weak relationship between total soil concentrations in soils and plants, it seems that the Sb bioavailability was limited and varied with different soil sites as well as plant species. Those observations would be significant to the phytoaccumulation and phytoremediation of plants and ecological and environmental risk assessment in Sb contaminated areas. (C) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
| Publication name |
MICROCHEMICAL JOURNAL Volume: 97 Issue: 1 Special Issue: Sp. Iss. SI Pages: 44-51 Published: JAN 2011 |
| Author(s) |
Qi, Cuicui, Wu, Fengchang, Deng, Qiujing, Liu, Guijian, Mo, Changli, Liu, Bijun, Zhu, Jing |
| Corresponding author |
WU Fengchang
wufengchang@vip.skleg.cn,lgj@ustc.edu.cn
1. Chinese Acad Sci, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Inst Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China
2. Chinese Res Inst Environm Sci, State Environm Protect Key Lab Lake Pollut Contro, Beijing 100012, Peoples R China |