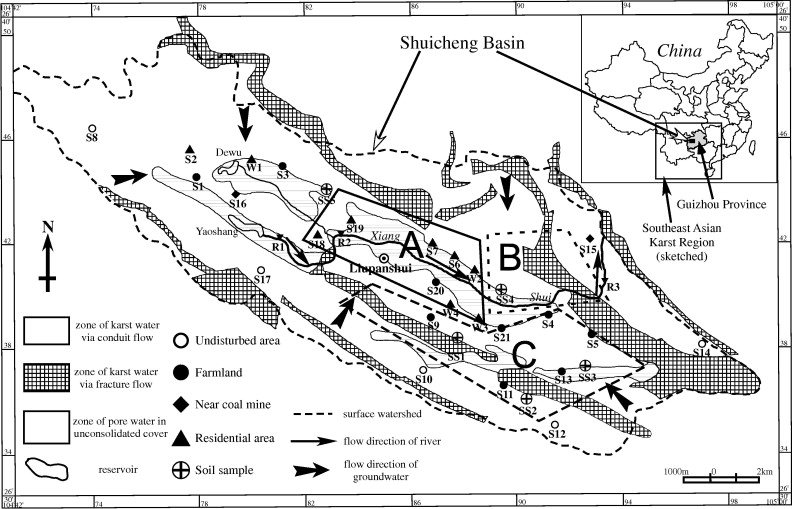
Fig. 1. Map showing sampling locations and sample numbers. In the map,
region “A” denotes the main urban and residential area, region “B” the industrial area, and region “C” the agricultural area.
Rapidly increasing populations, and associated intensification of agriculture, urbanization and industrialization, place increased demands on water resources and increased likelihood of pollution in many areas of the world. The Shuicheng Basin, southwestern China, is one such area and in order to understand water-rock interactions (carbonate dissolution) and anthropogenic impacts on groundwater quality in this karstic landform-dominated area, chemical as well as C, Sr and S isotopic compositions of groundwater (spring and well) and surface water (river) were measured during and following rainy seasons. The concentrations of various ions in groundwater were characterized by the dominant cations (Ca2+, Mg2+) and anions (HCO3-, SO42-), which account for more than 80% of the total ion concentration. Strontium isotope ratios (Sr-87/Sr-86, 0.70760-0.70918, mean 0.70831) and delta C-13(DIC) (-14.2 parts per thousand to -8.4 parts per thousand, mean -10.7 parts per thousand) indicate that the weathering dissolution of limestone controls Ca2+ and HCO3-. The decrease in delta C-13(DIC) values with increasing concentrations of anthropogenic species (Cl-, NO3- and Na+) shows that the C isotopic composition of DIC can be a useful tracer of contaminants. Chemical compositions, hydro-geological conditions and (delta S-34 analyses showed increasing SO42- concentration, resulting from domestic wastewater, fertilizer applications, atmospheric inputs through coal combustion, and oxidation of sulfide minerals, which typically are abundant in coal formations in the basin. Groundwater from the old downtown, industrial and agricultural areas exhibited high concentrations of Cl-, NO3-, SO42- and Na+, suggesting the groundwater is impacted by significant levels of contamination from human activities. (C) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
| Publication name |
APPLIED GEOCHEMISTRY Volume: 25 Issue: 12 Pages: 1924-1936 Published: DEC 2010 |
| Author(s) |
Li, Xiao-Dong; Liu, Cong-Qiang; Harue, Masuda; Li, Si-Liang; Liu, Xiao-Long |
| Corresponding author |
LI Xiaodong
lixiaodong@mails.gyig.ac.cn
Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Geochem, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, 46 Guanshui Rd, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Peoples |