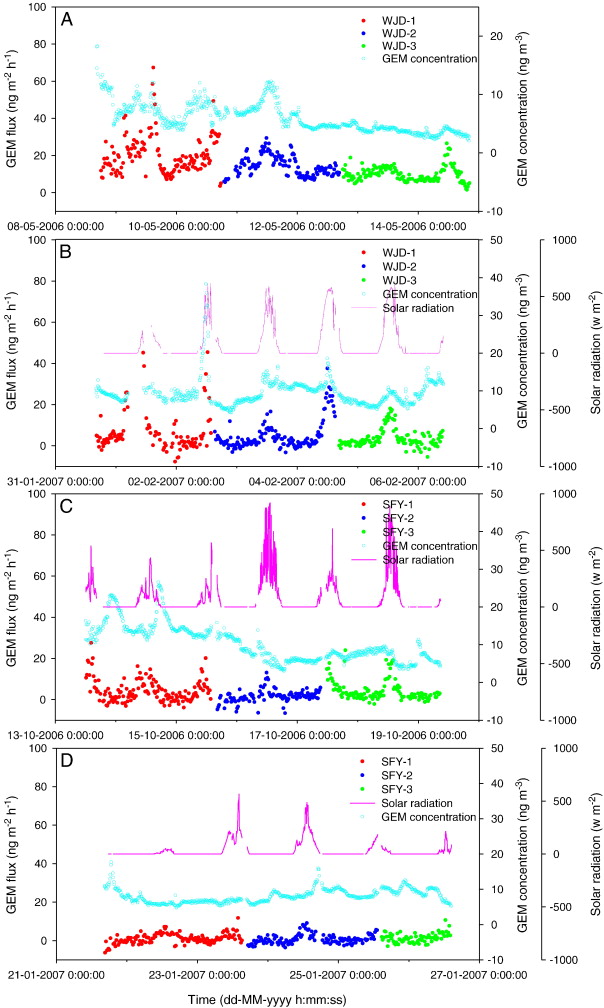
Fig. 2. Water/air GEM fluxes, GEM concentrations in ambient air above water surface and solar radiation in A) WJD in the warm season, (B) WJD in the cold season, (C) SFY in the warm season; and (D) SFY in the cold season.
Measurements of water/air exchange flux of gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) were conducted in a hyper-eutrophic reservoir and a meso-eutrophic reservoir in southwest China in both warm and cold seasons by using a dynamic flux chamber (DFC) method coupled with an automatic gaseous Hg analyzer. Both strong diurnal and seasonal variations of GEM fluxes were observed.
The diurnal cycle of the GEM flux was more pronounced during sunny days compared to cloudy and rainy days, which highlights the effect of solar intensity on the GEM flux. GEM fluxes in warm seasons were considerably higher (2.5 to 4.1 times higher) than in cold seasons, which was attributed to the combined factors including meteorological factors, water quality parameters and water Hg concentrations. Clear variation in GEM fluxes was observed between the two reservoirs. Mean GEM fluxes in the hyper-eutrophic reservoir (WJD) (3.2–20.1 ng m−2 h−1) were significantly higher than those in the meso-eutrophic reservoir (SFY) (0.6–4.4 ng m−2 h−1).
Evasion of Hg played a distinct role in the mass balance of Hg in the two reservoirs. In WJD, evasion was the second most important mechanism for Hg losses from the reservoir (17.5% of the total losses); whereas in SFY, loss of Hg via volatilization constituted an extremely little portion to the total losses of Hg (0.8%).
Keywords: GEM flux; Eutrophication; Subtropical reservoir; Spatial and temporal variation; Mass balance
| Publication name |
SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT Volume: 408 Issue: 23 Pages: 5887-5896 Published: NOV 1 2010 |
| Author(s) |
Fu, Xuewu; Feng, Xinbin; Wan, Qi; Meng, Bo; Yan, Haiyu; Guo, Yanna |
| Corresponding author |
FENG, Xinbin
Chinese Acad Sci, State Key Lab Environm Geochem, Inst Geochem, Guiyang 550002, Peoples R China |
View here for full text from the publisher